Last Updated on 9 months ago by Nicky Johnson
Viruses and bacteria are two types of microorganisms or microbes. They play a crucial role in our ecosystem. They have distinct differences and similarities between them.
While viruses and bacteria can cause infections and diseases, their structures, reproduction methods, and treatment options differ vastly.
Understanding these differences is essential in developing effective treatments for illnesses caused by either viruses or bacteria. In this article, we will explore how viruses are different from bacteria apexes.
We will also explore how these differences impact disease progression and treatment options for viral infections versus bacterial infections.
What are Viruses?
Blog Contents
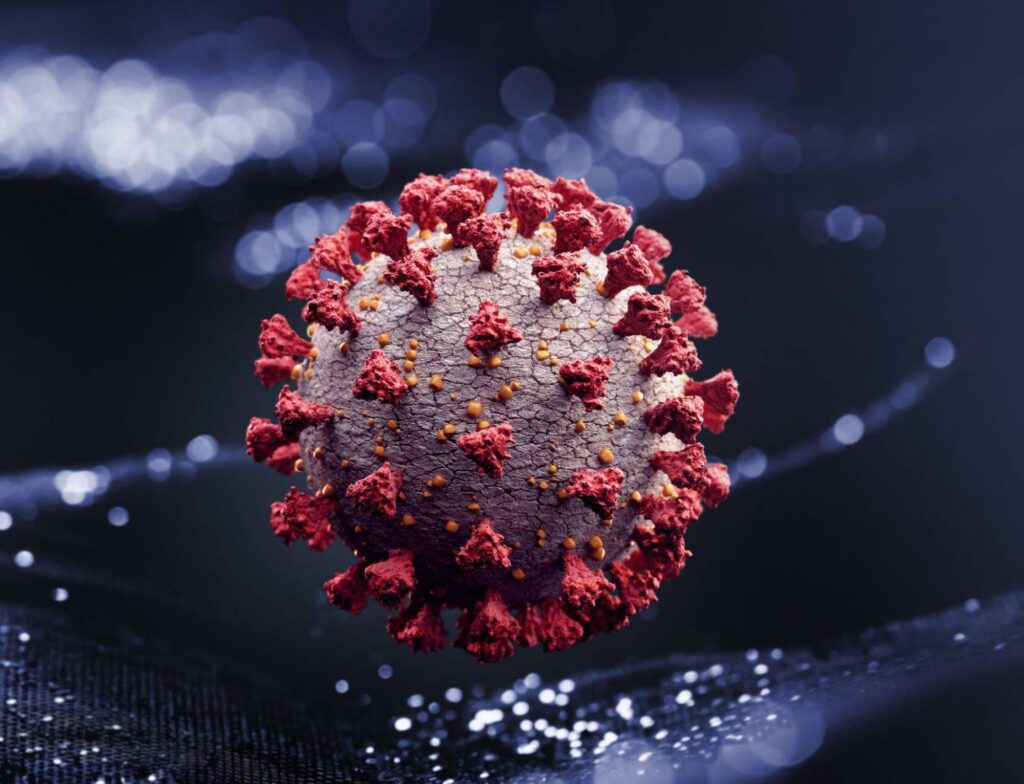
Viruses are infectious agents that can only replicate inside living cells. They have a simple structure consisting of a protein coat called the capsid, which encloses the genetic material.
Some viruses also have an additional layer outside the capsid known as the envelope, which helps them infect host cells.
Viruses are unique entities that lack cellular organelles and cytoplasm. Unlike other living organisms, they cannot perform metabolic activities on their own. Instead, viruses require a host cell to reproduce and spread.
The size of viruses is incredibly small, with some measuring just 20–30 nanometers in diameter. This makes them smaller than most bacteria and even some large molecules like proteins and lipids.
The small size of viruses allows them to easily penetrate through biological barriers such as cell membranes and enter host cells where they can initiate infection.
Despite their simplicity, viruses are capable of causing a wide range of illnesses in humans, including common colds, flu, hepatitis, HIV/AIDS, and COVID-19.
What are Bacteria?
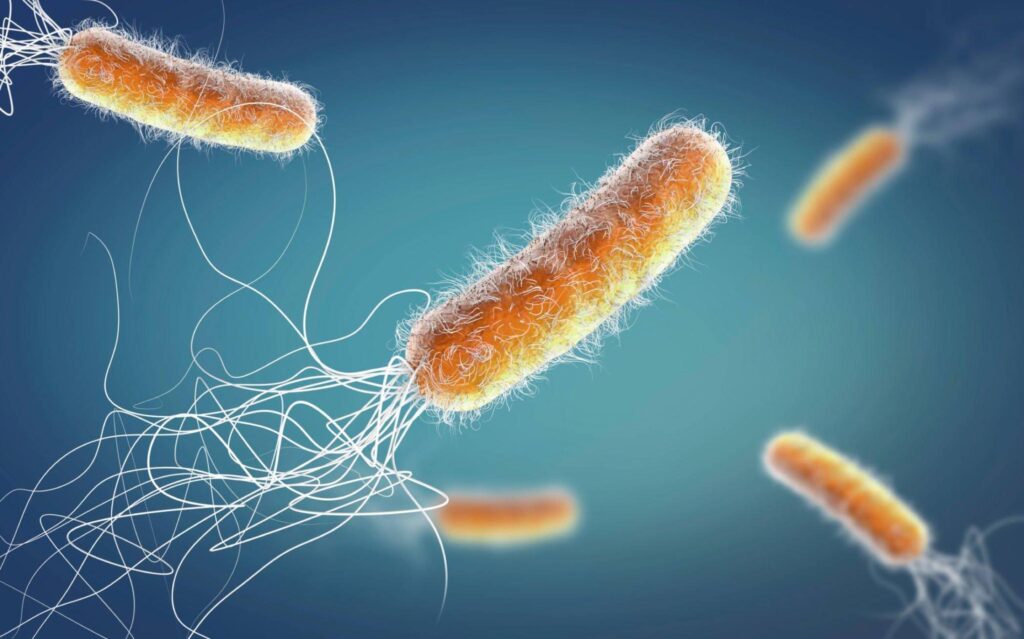
Bacteria are microbes that can survive in extreme environments. Some bacteria can even survive in the vacuum of space. One reason for their resilience is their small size and simple structure.
Bacteria also have a remarkable ability to form spores. This feature protects them from harsh conditions like heat, drought, and radiation.
They play a positive role in nitrogen fixation, decomposition of organic matter, and digestion. Bacteria are also used in biotechnology for producing medicines, enzymes, and other useful compounds.
Their diverse roles make them integral components of ecosystems and vital contributors to human health and wellbeing.
How Are Viruses Different From Bacteria Apex?
As discussed above, viruses and bacteria cause many diseases, like flesh-eating diseases. But the morphology, physiology, and anatomy of both are pretty different. Let’s see in detail;
Structure
The bacterial cell wall is a complex structure that is formed of peptidoglycan. It provides strength and rigidity to the cell. This feature is unique to bacteria and is absent in viruses. Unlike bacteria, viruses do not contain a cell wall.
Instead, they have a protein coat called a capsid. The capsid encloses its genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA. The capsid protects the viral genome from environmental factors such as heat, radiation, and chemicals.
Some viruses also have an additional envelope composed of lipids surrounding the capsid. The envelope allows the virus to interact with host cells more effectively but also makes them vulnerable to detergents and disinfectants.
Size
bacteria can be relatively large, ranging from 900 to 1000nm; viruses are much smaller, with a size range between 30 to 50nm.
Bacteria don’t require any host for survival. Viruses cannot survive outside of a host organism because they lack many necessary components for life processes.
Mode Of Reproduction
Bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission, where one cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This process is rapid and efficient for bacteria. Due to this, they can quickly colonize new environments and adapt to changing conditions.
However, because there is no exchange of genetic material between the parent and daughter cells during binary fission, bacterial populations may lack the genetic diversity necessary for long-term survival.
In contrast, viruses rely on host cells to replicate their genetic material. Once inside a host cell, viral DNA or RNA inserts itself into the host genome and commandeers the cellular machinery to produce multiple copies of itself.
These copies can then infect other cells within the same host or be released into the environment to infect new hosts. Because viruses require a host in order to replicate, they are considered obligate parasites.
Infections
Generally, localized infections are contained within a specific area of the body. The symptoms are limited to that area. Pneumonia is caused by bacteria that are usually confined to that area. It does not spread throughout the body.
While systemic infections affect multiple body parts, they can cause more severe symptoms. A typical example is influenza (flu), which affects the respiratory system and causes fatigue, muscle aches, and fever.
Systemic infections often require more aggressive treatment than localized infections because they have greater potential to spread.
Viruses and bacteria can both cause localized or systemic infections. They do so in different ways. Bacteria typically cause localized infections by multiplying in a specific body area and producing toxins that damage nearby tissues.
Viruses work differently; they invade cells throughout the body and use those cells’ machinery to replicate themselves. This often leads to systemic symptoms because a viral infection can affect many different types of cells.
Diseases
Bacterial diseases: these are pneumonia, meningitis, food poisoning, typhoid fever, and tuberculosis. Antibiotics are used to treat them.
Viral Diseases: these are the common cold, polio, smallpox, hepatitis A and B, AIDS (caused by HIV), and influenza.
While vaccines exist for some viral infections like polio and smallpox, treatments for viral infections are more limited than those available for bacterial infections.
Bacterial and viral infections are very different. But they have some similarities. Both types of infections can cause similar symptoms. Bacteria cause bacterial infections, while viruses cause viral infections.
One way in which bacterial and viral infections can be related is through secondary infections. A person may contract a viral infection like the flu or pneumonia. Their immune system may become weakened.
It becomes more susceptible to bacterial infection. This can lead to a secondary infection that worsens their overall condition. For example, severe cases of viral pneumonia can sometimes end up with an associated bacterial infection that further complicates treatment.
Doctors often use medical history, physical exams, and laboratory tests for identification. Doctors will ask questions about symptoms for medical history. They may also inquire about recent travel or exposure to sick individuals.
Doctors may order laboratory tests such as blood or urine cultures to confirm their initial diagnosis and determine whether antibiotics are necessary. These tests identify the presence of bacteria in the body.
They determine which antibiotics would be most effective if needed. In some cases, spinal cultures may also be ordered if there is suspicion of meningitis or other serious infections affecting the central nervous system.
In many cases, a medical history and physical exam may be enough for examination. Additionally, some infections may have similar symptoms. It makes it difficult to differentiate without additional testing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bacteria are single-celled organisms that can live independently. Viruses require a host cell to replicate themselves. Moreover, viruses do not have their own metabolic machinery.
They cannot grow or reproduce outside a host organism. These differences make it challenging to treat viral infections compared to bacterial ones. Scientists are continuously developing new ways to target and eliminate viruses.
As we continue to explore the vast and intriguing world of microorganisms, let’s remember the importance of staying informed and vigilant against these tiny but mighty foes.